Problem 65
The illustration below depicts an alternative layout method.
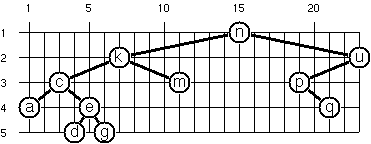 Find out the rules and write the corresponding function. Hint: On a given level, the horizontal distance between neighboring nodes is constant. Write a function to annotate each node of the tree with its position.
Find out the rules and write the corresponding function. Hint: On a given level, the horizontal distance between neighboring nodes is constant. Write a function to annotate each node of the tree with its position.
To solve this problem you will need to traverse the tree. Problems 68a, 68b, and 68c examine tree traversal.
Example
tree65 =
Node 'n'
(Node 'k'
(Node 'c'
(Node 'a' Empty Empty)
(Node 'e'
(Node 'd' Empty Empty)
(Node 'g' Empty Empty)))
(Node 'm' Empty Empty))
(Node 'u'
(Node 'p'
Empty
(Node 'q' Empty Empty))
Empty)
layout65 tree65 ==
Node ('n',(15,1))
(Node ('k',(7,2))
(Node ('c',(3,3)) ...
Unit Test
import Html
import List
type Tree a
= Empty
| Node a (Tree a) (Tree a)
tree65 =
Node 'n'
(Node 'k'
(Node 'c'
(Node 'a' Empty Empty)
(Node 'e'
(Node 'd' Empty Empty)
(Node 'g' Empty Empty)))
(Node 'm' Empty Empty))
(Node 'u'
(Node 'p'
Empty
(Node 'q' Empty Empty))
Empty)
{-| Given a Tree return a tree that adds x, y coordinates for each node
to layout a graphic representation of the tree
-}
layout : Tree comparable -> Tree ( comparable, (Int, Int) )
layout tree =
-- your implementation goes here
Empty
main =
Html.text
(if (test) then
"Your implementation passed all tests."
else
"Your implementation failed at least one test."
)
test : Bool
test =
let
t = layout tree65
in
List.all ((==) True)
[ t == layout65
]
layout65 =
Node ('n', (15, 1))
(Node ('k', (7, 2))
(Node ('c', (3, 3))
(Node ('a', (1, 4)) Empty Empty)
(Node ('e', (5, 4))
(Node ('d', (4, 5)) Empty Empty)
(Node ('g', (6, 5)) Empty Empty)))
(Node ('m', (11, 3)) Empty Empty))
(Node ('u', (23, 2))
(Node ('p', (19, 3))
Empty
(Node ('q', (21, 4)) Empty Empty))
Empty)
Hints
- Find out the rules and write the corresponding function. Hint: At a given depth, the horizontal distance between neighboring nodes is constant.
- Need another hint? The horizontal distance is a function of the depth from the tree from that node and the depth of the left subtree.